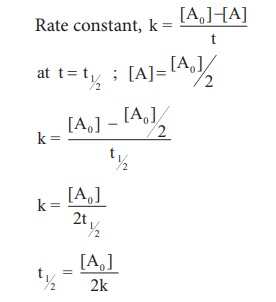
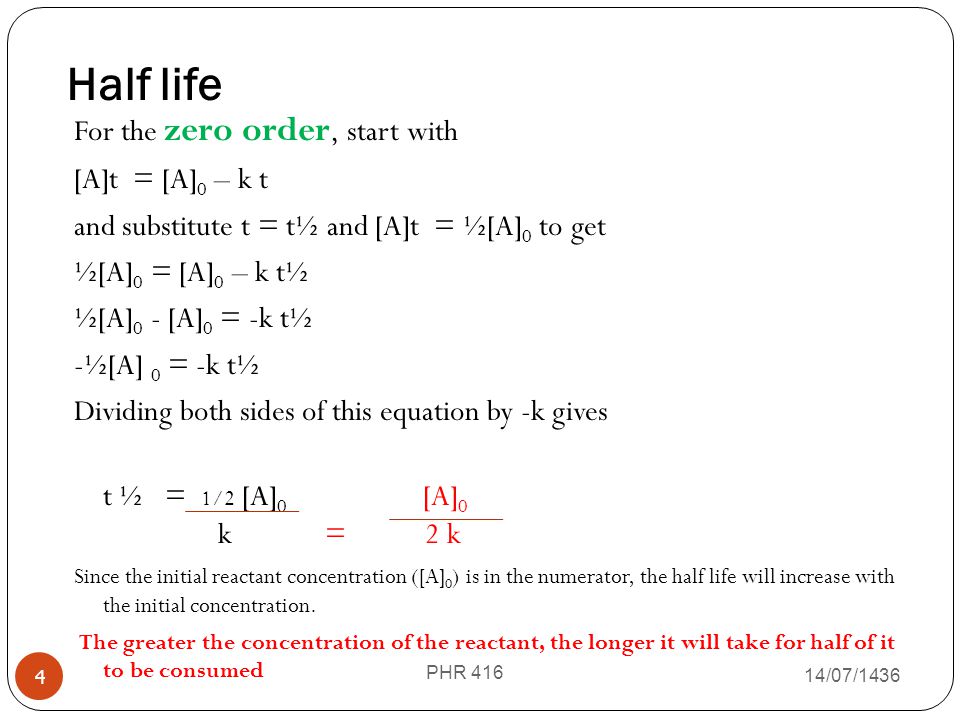
half life formula for zero order reaction
Therefore A2 k 0 t ½ or t ½ A2k. As for other reaction orders an equation for zero-order.
Relationship Between Half-life and Zero-order Reactions.

. Equations for Half Lives. T_12 is a timescale in which each half-life represents the reduction of the initial population to 50 of its original state. T ½ 1 k A o Top.
The equation indicates that the smaller the A 0 the shorter the half-life or in other words the half-life of a zero-order reaction gets shorter as the concentration decreases. Latext_frac12 fracA_02klatex A 0 represents the initial concentration and k is the. The half-life equation for a zero-order reaction is latext_frac12fracA_02klatex.
T ½ A o 2k For a first order reaction A products rate kA. We can represent the relationship by the following equation. 5 rows Zero-Order Reactions.
Plotted against t time. Given below is the half-life of a zero-order reaction. T ½ x2k where x initial concentration of reactant.
The Half-Life of Zero Order Reaction calculator computes the half-life in nuclear decay for a zero order reaction. The formula for half-life in chemistry depends on the order of the reaction. From the above-integrated equation we have.
T 1 2 1 k A 0 b. Half-life of Zero-order Reactions. 2 The unit of rate constant K is mole litre-1 time-1.
Thus for a first-order reaction each successive half-life is the same length of time as shown in. 11Half-lifeNumber of half-lives elapsedFraction remainingPercentage remaining0111122143185. For a first order reaction t½ 0693 k and for a second order reaction t½ 1 k Ao.
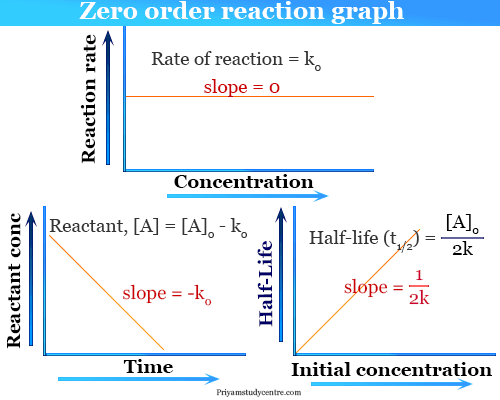
Replace t with half-life t 12. Characteristics of zero order reaction-1 The concentration of the product increases linearly with time. What is a 0 in half-life.
Graphical relations and half lives. The rate constant for the reaction can be determined from the slope of the line which is equal to -k. For the first-order reaction the half-life is defined as t 12 0693k.
The half-life of a reaction describes the time needed for half of the reactants to be depleted which is the same as the half-life involved in nuclear decay a first-order reaction. T 12 is the half-life of the reaction seconds. Determine the half-life of a zero order react.
2 k t 1 2. The half-life of the reaction is denoted by t 12 and is expressed in seconds. Remember the half-life of a reaction changes with the order of the reaction.
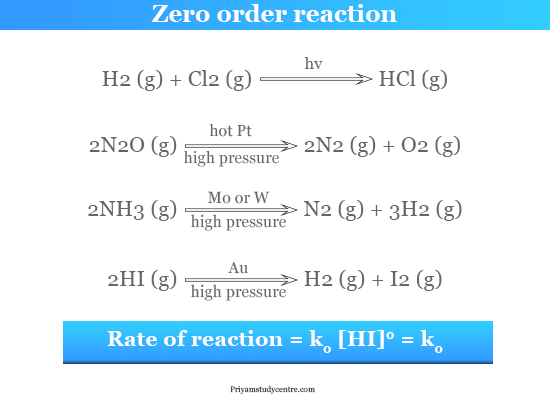
T 1 2 k ln 2 c. For a first order reaction t½ 0693 k and for a second order reaction t½ 1 k Ao. And the reason for this is that most zero-order reactions either require a catalyst or occur between gases in saturated containers.
T 1 2 05 k e. T 12 is the half-life of the reaction seconds. ½ A A 0 kt 12.
Half life in zero order reaction. 453 t 1 2 0693 k. A straight line passing through origin is obtained when x is.
From the above formula the half-life of the zero order kinetics depends on the initial concentration of the reactant. Half life means 50 percent of reactants disappear in that time interval. It is to be noted that the formula for the half-life of a reaction varies with the order of the reaction.
When t t ½ that is the half-life of the reaction completed the concentration of the reactant A A2. T 1 2 A 0 2 k d. 2 0693 into the equation results in the expression for the half-life of a first-order reaction.
Now replacing t with half-life t12 in the above equation. The mathematical expression that can be employed to determine the half-life for a. For a zero order reaction A products rate k.
Converting a half life to a rate constant. The half-life equation for a zero-order reaction is t12A02k t 1 2 A 0 2 k. Determining a half life.
T ½ 0693 k For a second order reaction 2A products or A B products when A B rate kA 2. 3 The time required for the reaction to be complete i-e time at which A is zero. Remember the half-life of a reaction changes with the order of the reaction.
For a zero order reaction the formula is t½ Ao 2k. And for the second-order reaction the formula for the. Because this equation has the form y mx b a plot of the concentration of A as a function of time yields a straight line.
A A 0 - kt. Term half-lifeThe time required for a quantity to fall to half its value as measured at the beginning of the time period. The mathematical expression that can be employed to determine the half-life for a zero-order reaction is t 12 R 0 2k.
A A 0 - kt. The half-life of a Zero-th order reaction is t A0 2kHere I derive this from the Integrated Rate LawAsk me questions. For a zero-order reaction the half-life is given by.
Which of the following corresponds to the correct equation for the half-life of a zero-order reaction. The integrated rate law for the zero-order reaction A products is A_t -kt A_0. 12 A A 0 - k t 12 k t 12 12 A 0 t 12 12 k A 0 t 12 A 0 2k.

Half Life Of Zero Th 0th Order Reaction Derivation Youtube

Zero Order Reactions Video Kinetics Khan Academy

Half Life Expressions Chemistnate
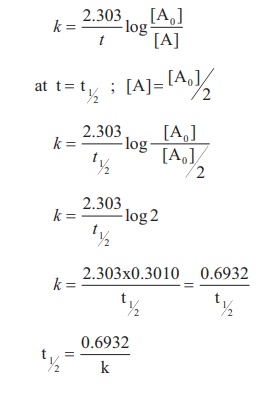
Half Life Period Of A Reaction Chemical Kinetics

Rate Of Zero Order Reaction Integrated Law Half Life Period Rate Constant
Zero Order Reaction Definition Examples Formula

Derive The Integrated Half Life Equation For Zero Order Reaction Chemistry Chemical Kinetics 12889537 Meritnation Com
Zero Order Reaction Definition Examples Formula

Half Life Expressions Chemistnate
A Derive The General Form Of The Expression For The Half Life Of A First Order Reaction Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community

Integrated Rate Laws Chemistry For Majors

Kinetics And Drug Stability Ed

Chapter 14 Chemical Kinetics And Stability Skku Physical
Principles And Kinetics Of Drug Stability Phr 416 Ppt Video Online Download

Zero Order Reactions Chemistry Class 12 Iit Jee Main Advanced Neet Aipmt Askiitians Youtube